Wilson's Disease
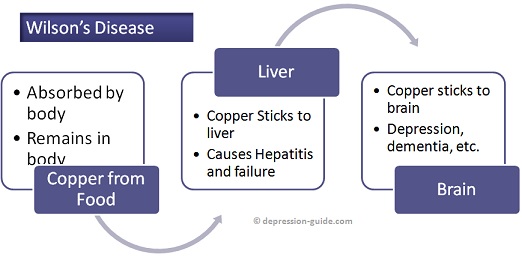
TweetWilson’s disease is a rare genetic disorder which is caused by copper buildup. It is also known as hepatolenticular degeneration. Very small amount of copper is present in our body which is released in the urine regularly. If this cannot leave the body, it deposits in some organs in the body like liver and kidney. This is what which happens in Wilson's Disease.
The major places where copper build up happens in Wilson's Disease is Liver and Brain. If the deposit occurs in brain, then there are different neurological issues which start to occur. If the deposit happens in liver, then it could lead to liver and kidney failure.
Wilson's disease starts to showup when the person is about 13-24 year old. It starts in early adolescence. The major body part affected, almost in more than 60% of Wilson's Disease cases, is liver. Initally, the only physical changes happening in liver will be visible only under microscopr. Then the Wilson disease hepatitis occurs which usually is misinterpreted as infectious hepatitis. Testing of the unexplained hepatitis is needed in such cases.
Symptoms of Wilson's disease
Some of the Physical symptoms of Wilson's disease are as follows:
1. Odd tremors in the arms,
2. slowness in body movement
3. Cannot speak properly
4. Issue with writing with hand
5. Walk becomes unsteady
6. Headache
7. Seizures
Psychological symptoms also occur. They can be mood swings, concentration issues and depression. Personality change is also seen in many people.
It can lead to permanant musculur weakness, dementia, etc.
Causes of Wilson Disease
It is caused by inherited autosomal change in ATP7B gene. The child who suffers from wilson disease takes the gene from both the parents. the chances of inheriting autosomal recessive mutations from both the parents is one in 4. If only one parent transfers the gene, then the child becomes the carrier of the disease and passes it to the next generation.
Treatment of Wilson's Disease
This disease is treatable. But it need to start as early as possible. Since the progression of Wilson Disease can cause permanant damage to brain or liver, causing organ failure and even death.
The different options of treatment include medications, changes in diet and nutrition. In some cases, liver transplant may also be needed.
Chelating agents are used to remove extra copper from the body and which is deposited in organs. Copper is released to the blood stream and then it is passed in the urine by the kidney. Penicillamine and Trientine are two of the chelating agents used to treat wilson disease. Zinc has the capability to stop the absorption of more copper in the body. It does not remove already present copper, but does not allow more copper to be added.


Sometimes crying or laughing
are the only options left,
and laughing feels better right now.

Current Issue
 Self Help Leaflets Take the help of our self help leaflets or booklets. |
 The DG Magazine All about living with depression |
Brain Disorders
Brain Disorders
- Transverse myelitis
- Chiari malformation
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Coma
- Concussion
- Encephalitis
- Delirium
- Essential Tremor
- Post Concussion Syndrome
- Brain Tumor
- Intracranial Hematoma
- Transient global amnesia
- Reye's syndrome
- Autonomic neuropathy
- Bell's palsy
- Acoustic neuroma
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)
- Brachial plexus injury
- Cerebral palsy
- Charcot Marie Tooth disease
- Complex regional pain syndrome
- Dystonia
- Foot drop
- Guillain-Barre syndrome
- Krabbe disease
- Meniere's disease
- Myasthenia gravis
- Optic neuritis
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Phantom pain
- Post-polio syndrome
- Postherpetic neuralgia
- Progressive supranuclear palsy
- Ramsay Hunt syndrome
- Spasmodic torticollis
- Spinal cord injury
- Spinal stenosis
- Trigeminal neuralgia
- Vocal cord paralysis
- Whiplash
- Primary progressive aphasia
- Leukodystrophies
- Wilson's Disease
- Aneurysm
- Aphasia












