Brain Disorder
TweetOur Brain is the primary source of all our behaviour and body functions. It gives us ability to think, memorize, control, etc. Any injury or any genetic illness can severely impact brain functioning and hence can cause Bran Disorders. The section below deals with different type of brain disorders and the way forward for them.
Brain Disorders aims to provide a resource for people newly-diagnosed with brain-related disorders, their friends and relatives, and health professionals. Brain injury is the term often used when referring to traumatic brain injury.
Top Stories in Brain Disorders
 Reye's syndrome - Reye syndrome is most often seen in children ages 4 - 12. Most cases that occur with chickenpox are in children ages 5 - 9. Reye's syndrome - Reye syndrome is most often seen in children ages 4 - 12. Most cases that occur with chickenpox are in children ages 5 - 9. |
 Bell's palsy- What is Bell's palsy? Bell's palsy is a paralysis or weakness of the muscles on one side of your face. Bell's palsy- What is Bell's palsy? Bell's palsy is a paralysis or weakness of the muscles on one side of your face. |
|
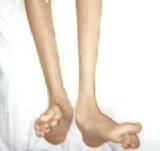 Charcot Marie Tooth disease - Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) is one of the most common inherited neurological disorders, affecting approximately 1 in 2,500 people in the United States Charcot Marie Tooth disease - Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) is one of the most common inherited neurological disorders, affecting approximately 1 in 2,500 people in the United States |
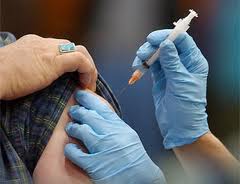 Guillain-Barre syndrome - Comprehensive overview covers symptoms, treatment of this group of peripheral nerve disorders. Guillain-Barre syndrome - Comprehensive overview covers symptoms, treatment of this group of peripheral nerve disorders. |
|
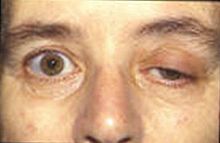 Myasthenia gravis - Myasthenia gravis - Learn about myasthenia gravis, a neuromuscular disease which symptoms include eye weakness, facial expression weakness, and difficulty swallowing. |
 Post-polio syndrome - Post-polio syndrome - Post-polio syndrome (PPS) is the onset of new deterioration in function that may occur many years after recovery from acute poliomyelitis. |
More on Brain Disorders
- Transverse Myelitis
- Chiari Malformation
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Coma
- Concussion
- Encephalitis
- Delirium
- Essential Tremor
- Post Concussion Syndrome
- Brain Tumor
- Intracranial Hematoma
- Transient global amnesias
- Reye's syndrome
- Primary progressive aphasia
- Prolactinoma
- Pseudotumor cerebri
- Leukodystrophies
- Wilson's Disease
- Aneurysm
- Aphasia
Nerve and muscle disorders
- Autonomic neuropathy
- Bell's palsy
- Acoustic neuroma
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)
- Brachial plexus injury
- Cerebral palsy
- Charcot Marie Tooth disease
- Complex regional pain syndrome
- Dystonia
- Foot drop
- Guillain-Barre syndrome
- Krabbe disease
- Meniere's disease
- Myasthenia gravis
- Optic neuritis
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Phantom pain
- Post-polio syndrome
- Postherpetic neuralgia
- Progressive supranuclear palsy
- Ramsay Hunt syndrome
- Spasmodic torticollis
- Spinal cord injury
- Spinal stenosis
- Trigeminal neuralgia
- Vocal cord paralysis
- Whiplash
Genetic Brain Disorders
A genetic disorder is a disease caused by a different form of a gene, called a variation, or a change in a gene, called a mutation. Genetic brain disorders specifically affect the development and function of the brain.
Some examples of genetic brain disorders include leukodystrophies, phenylketonuria, Tay-Sachs disease, and Wilson disease.


Sometimes crying or laughing
are the only options left,
and laughing feels better right now.

Current Issue
 Self Help Leaflets Take the help of our self help leaflets or booklets. |
 The DG Magazine All about living with depression |
Brain Disorders
Brain Disorders
- Transverse myelitis
- Chiari malformation
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Coma
- Concussion
- Encephalitis
- Delirium
- Essential Tremor
- Post Concussion Syndrome
- Brain Tumor
- Intracranial Hematoma
- Transient global amnesia
- Reye's syndrome
- Autonomic neuropathy
- Bell's palsy
- Acoustic neuroma
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)
- Brachial plexus injury
- Cerebral palsy
- Charcot Marie Tooth disease
- Complex regional pain syndrome
- Dystonia
- Foot drop
- Guillain-Barre syndrome
- Krabbe disease
- Meniere's disease
- Myasthenia gravis
- Optic neuritis
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Phantom pain
- Post-polio syndrome
- Postherpetic neuralgia
- Progressive supranuclear palsy
- Ramsay Hunt syndrome
- Spasmodic torticollis
- Spinal cord injury
- Spinal stenosis
- Trigeminal neuralgia
- Vocal cord paralysis
- Whiplash
- Primary progressive aphasia
- Leukodystrophies
- Wilson's Disease
- Aneurysm
- Aphasia












